Hazardous waste

Mixed Hazardous Construction Waste: Managing Risk on Demolition and Renovation Sites
13.07.25
Other construction and demolition waste (including mixed waste) containing hazardous substances (17 09 03)* includes materials like paints, adhesives, asbestos fragments, solvents, heavy metals, and chemical residues. Hazardous waste management requires identifying components, classifying hazards, and documenting the handling process.

Infectious Medical Waste: Managing Risk Through Strict Sanitary Control
09.07.25
Waste requiring special collection and disposal methods to prevent infection arises in clinics during treatment, vaccination, and laboratory procedures involving contagious patients or biohazards. Hazardous waste management involves strict separation, labeling, documentation, and traceability from source to disposal.

Hazardous Medical Chemicals: Control and Environmental Safety
06.07.25
Chemical preparations consisting of or containing hazardous substances (18 01 06)* are used in healthcare for sterilization, diagnostics, and laboratory work. Mishandling can cause environmental and health risks. Hazardous waste management includes categorization, quantity tracking, and registration in compliance documents.
Cytotoxic and Cytostatic Drugs: Managing Highly Hazardous Medical Waste
03.07.25
Cytotoxic and cytostatic drugs (18 01 08, 18 02 07)* are used in chemotherapy and pose severe risks due to their mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. They are considered highly hazardous waste. Hazardous waste management requires documentation and classification immediately upon identification of the substance.

Dental Amalgam Waste: Safe Mercury Waste Handling in Clinics
30.06.25
Amalgam waste from dental use (18 01 10)* is classified as hazardous due to mercury content. It arises from filling applications, removal of old fillings, and cleaning of amalgam separators and tools.
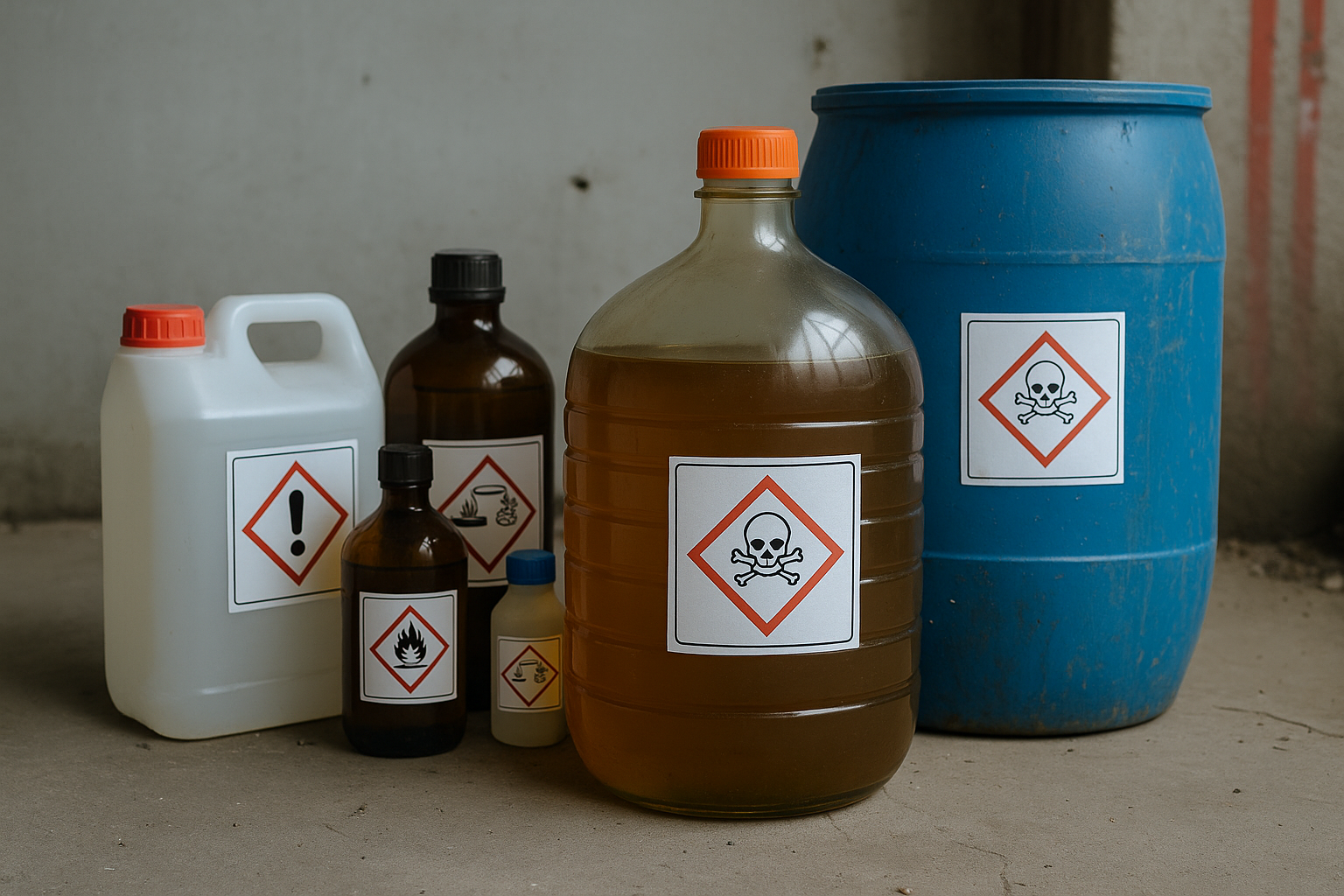

Hazardous Chemical Substances: Safe Industrial Management
26.06.25
Chemical substances consisting of or containing hazardous components (18 02 05)* include acids, solvents, reagents, and toxic materials commonly found in laboratories, industry, and healthcare.
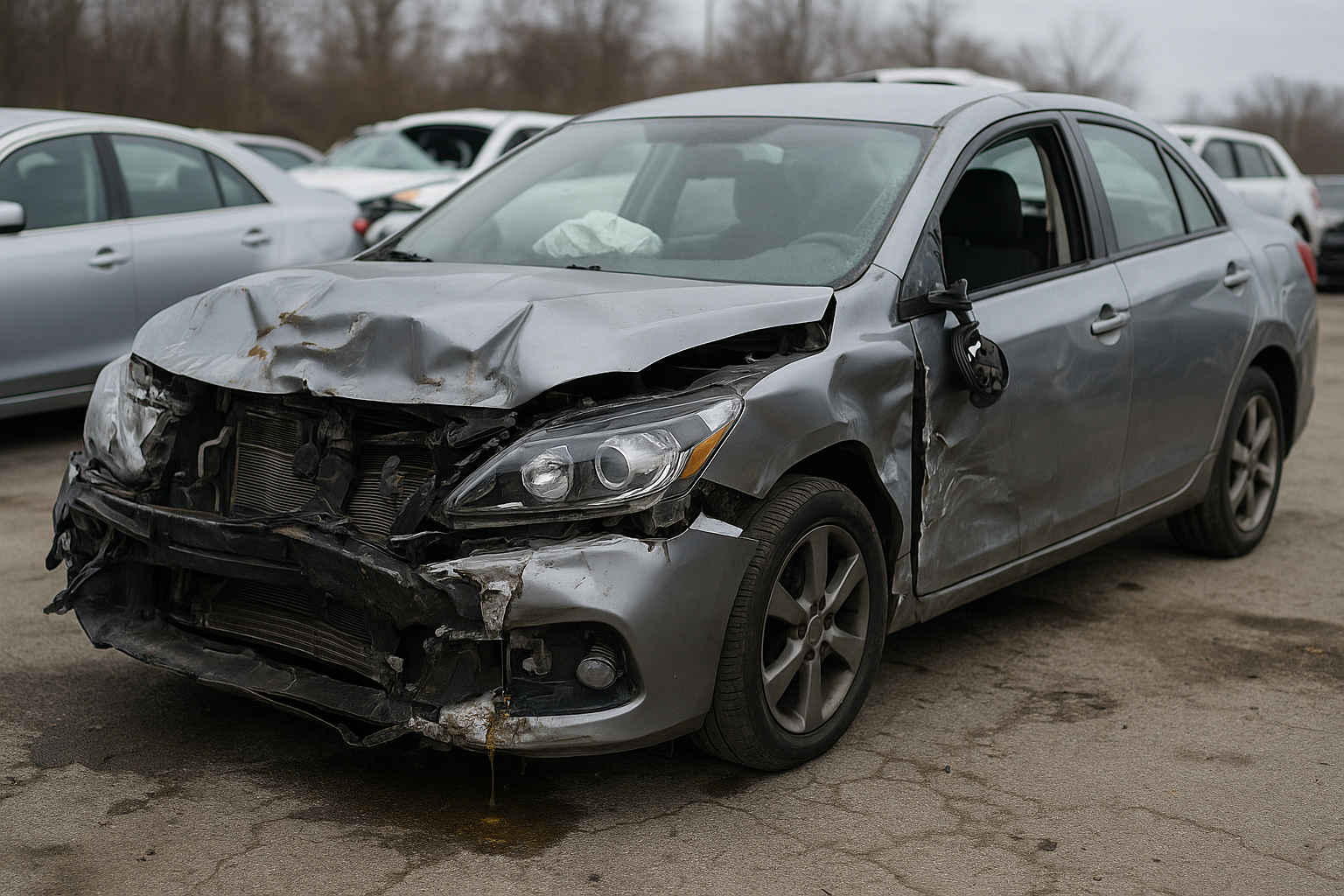

Damaged Vehicles as Hazardous Waste Sources: Safe Handling Practices
23.06.25
Damaged vehicles (16 12 52)* often contain hazardous waste such as fuel residues, oils, brake fluids, batteries, filters, airbags, and toxic electronics.
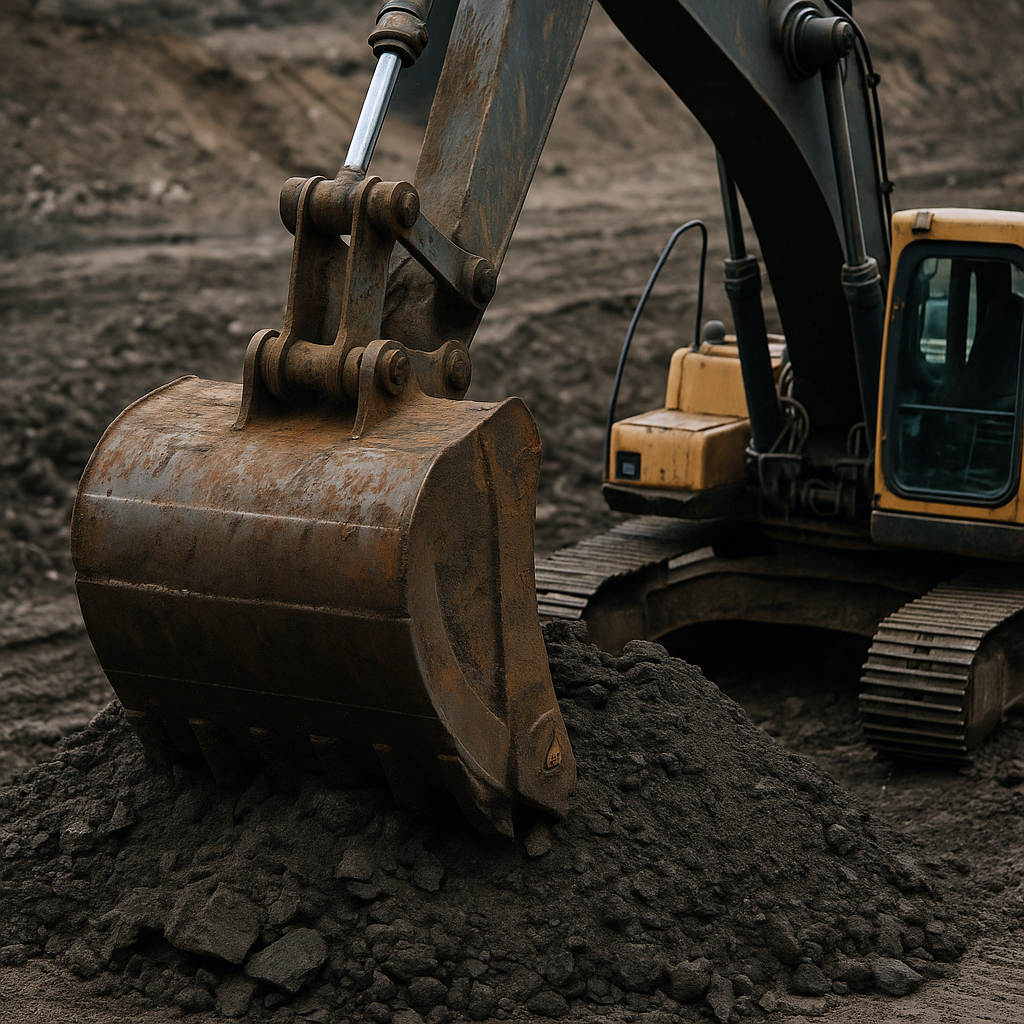

Spoil from Earthworks Containing Hazardous Substances: Managing Soil Risks
20.06.25
Spoil from earthworks containing hazardous substances (17 05 05)* results from excavation and site preparation in construction, mining, and large-scale development. Such material may include oil residues, heavy metals, and industrial contaminants.
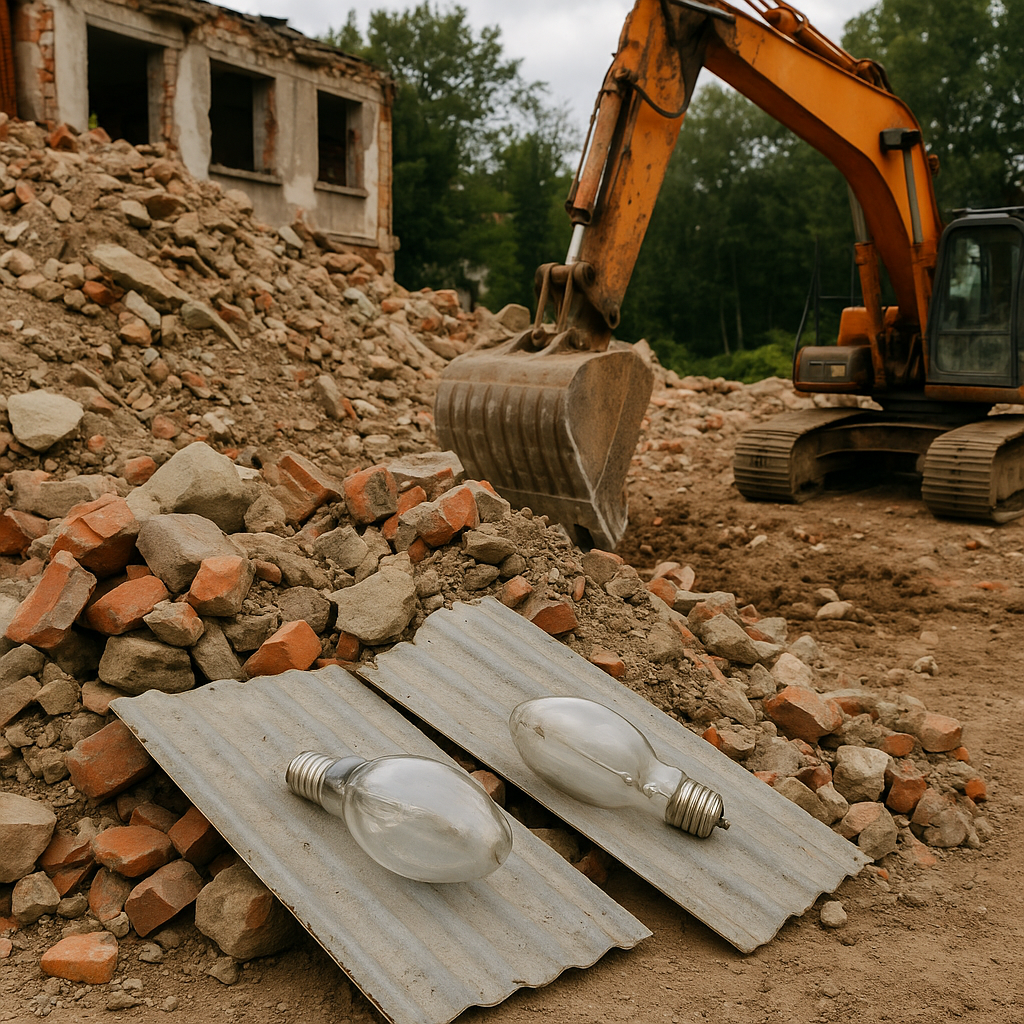

Mercury-Contaminated Construction Waste: Managing Demolition Hazards
16.06.25
Construction and demolition waste containing mercury (17 09 01)* is produced when dismantling buildings with mercury-based materials like thermostats, fluorescent lamps, and coatings.
Waste Search
Calculate cost?
Calculate processing cost for